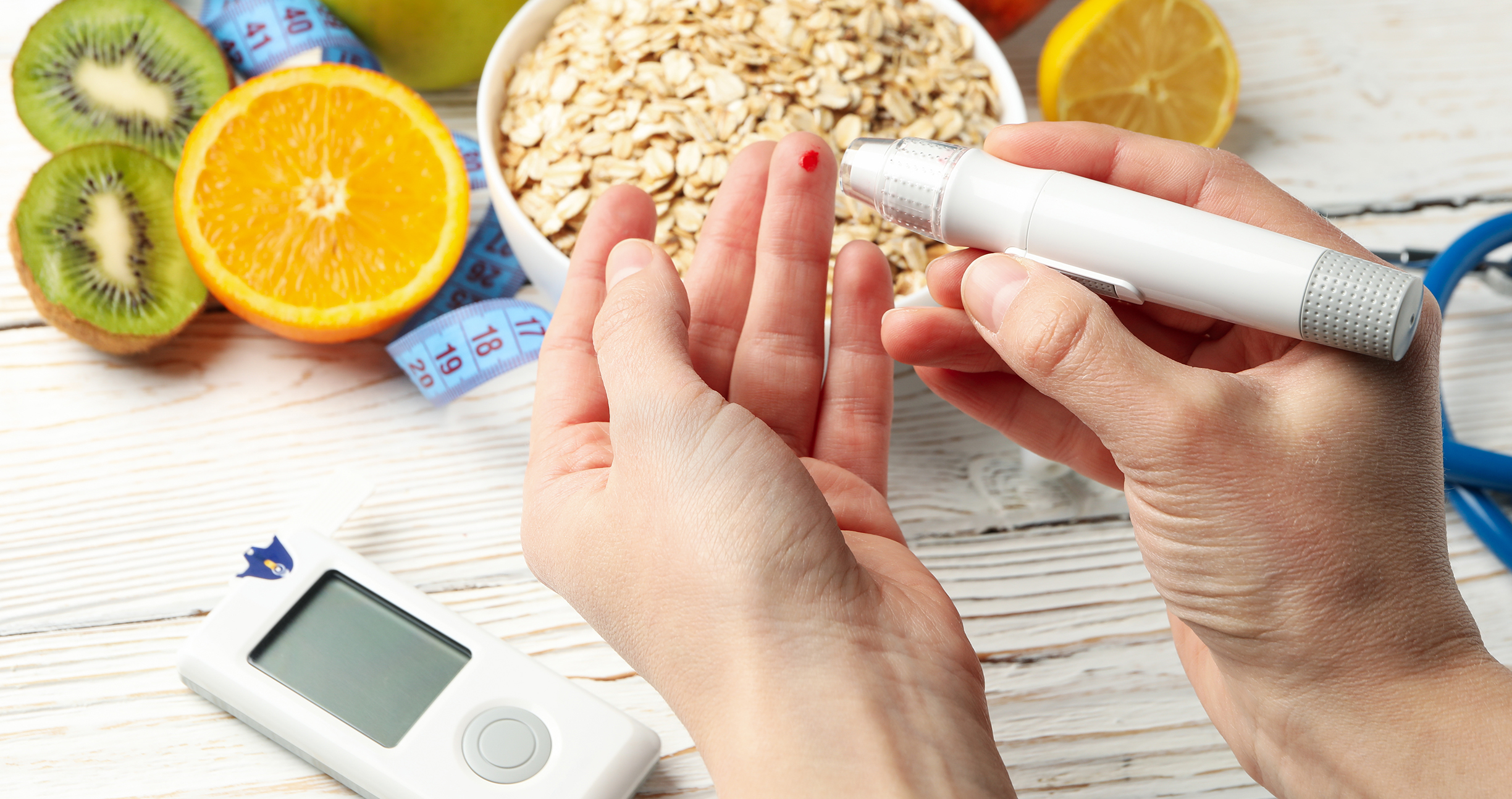
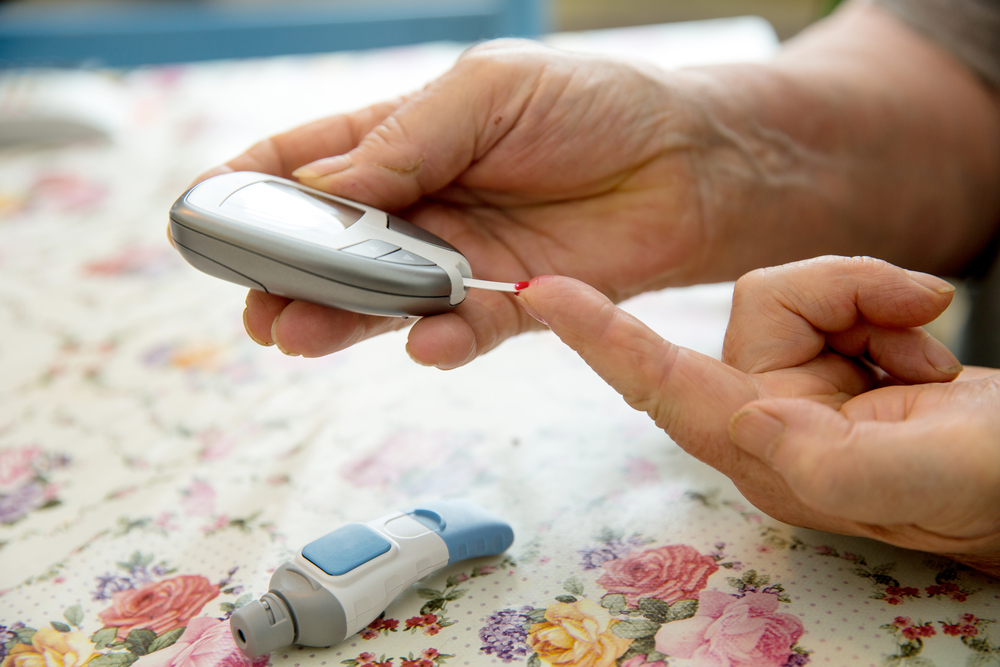
Diabetes can cause gradual, unassuming symptoms that can sneak up on you. Frequent urination and excessive thirst are the telltale signs of type 2 diabetes mellitus. These signs of diabetes are often mild and can easily be attributed to other factors.
Diabetes mellitus is a serious metabolic condition affecting people of all geographic, ethnic, or racial origins, and its prevalence is increasing across the world. It is a chronic condition that causes glucose levels in the body to rise. If not diagnosed or treated, diabetes can cause heart disease, nerve damage, stroke, kidney damage, vision loss, and more. Even if you have mild elevated sugar levels, you can damage your organs. Type 2 diabetes has an asymptomatic period of sub-clinical stages, which often remains undiagnosed for several years. As a result, in a lot of patients, vascular effects are already present at the time of diagnosis of diabetes, which is often recognized at the time of opportunistic testing.
Generally, the Asian population has a high risk of developing diabetes at a very young age as compared to the Western population. Therefore, efforts must be made to diagnose diabetes early so that the long-term suffering of the patients can be considerably mitigated. This blog discusses early warning signs of type 2 diabetes. Even if you have subtle symptoms, it is worth mentioning them to your healthcare provider, especially if you are at risk for diabetes. The higher the sugar level and the longer you live without treatment, the further damage can be done.
Types of diabetes
Normally, our body utilizes insulin to help muscle and fat cells take up glucose for energy. Diabetes stops using insulin effectively in your body when you have diabetes, which allows blood sugar to build up in your bloodstream.
Type 1 diabetes: It occurs when the pancreas fails to produce insulin, and the immune system destroys the cells that produce it. Also known as juvenile diabetes, it can occur at any age.
Type 2 diabetes: It develops when your cells do not respond as well to insulin as they normally do, and additional insulin is required to attain the same effect. This type of diabetes mainly affects adults.
Gestational diabetes: It occurs when a pregnant woman’s hormones affect her ability to produce enough insulin hormone for her body. However, an estimated 7% of women develop gestational diabetes.
Warning signs and classic symptoms of diabetes
Considering the symptom-free nature of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the early stages, people must be educated on its warning signs. The classic diabetes symptoms, including excessive thirst, extreme hunger, and large urine production, occur commonly in people with type 1 diabetes, which has a rapid development of severe hyperglycemia, and in people with type 2 diabetes with very high levels of hyperglycemia. In type 1 diabetes, severe weight loss is commonly reported, as if type 2 diabetes remains undetected for a long period. Fatigue, restlessness, body pains, and unexpected weight loss are also common signs of undetected diabetes.
-
- Excessive thirst – Frequent urination can cause dehydration, making you feel thirsty more often. But in this case, drinking more doesn’t satisfy the thirst. In this case, you only going to the bathroom more.
- Frequent urination – Visiting the toilet more than normal, especially at night, is a symptom of high blood sugar. When you have diabetes, your kidney needs to work harder to eliminate excess sugar from your bloodstream. When your kidneys can’t keep up, they spill excess glucose (sugar) into your urine, leading to more frequent urination.
- Constant hunger – Our body converts the food you eat with the glucose your body cells use for energy. But, if you have diabetes, the cells can’t absorb glucose correctly, so your body can’t receive enough energy from the food you eat. Therefore, your body is constantly looking to boost energy, and you will always feel hungry, even if you have just finished the meal.
- Repeat infections – Excess sugar in urine feeds yeast and bacteria. The presence of excessive glucose circulating in your body can lead to the development of yeast overgrowth in men and women. Some people, especially women with diabetes, often experience frequent urinary tract or yeast infections.
- Unexplained weight loss – If your body cannot get enough energy from processing the sugar in your food, you may notice an unusual increase in your appetite or sudden and unexpected weight loss.
- Weakness – Extreme weakness, sleepiness, or lethargy can show that your blood sugar hits you hard. A sudden rise or drop in blood sugar can cause dizziness or fainting. Weakness hits so hard that some people become so weak that they lose consciousness and are not able to gain consciousness again. This condition is referred to as diabetic coma, and it can be deadly.
- Slow-healing cuts – High blood sugar levels can cause stiffness in your blood vessels, making it tough for the blood to flow around your body. Poor blood circulation means that little sores heal more quickly.
- Dry mouth or dry skin – Dehydration can make your mouth feel dry, your skin excessively dry, and your hair itchy or tight.
- Pain or numbness in extremities – Diabetes patients may experience nerve damage due to elevated blood sugar and fat levels. This condition is known as diabetic neuropathy. You might experience tingling in your hands and feet. Nerve damage can severely affect internal organs, such as your bladder.
- Vision changes – Vision changes are commonly associated with diabetes. If not treated at the right time or poorly managed, diabetes can ultimately affect vision and even lead to blindness.
Most people with diabetes don’t know they have high blood sugar levels until they are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes.
Regular testing is key to avoiding diabetes-associated complications.
Because the symptoms can be subtle, you must see your healthcare specialist regularly for checkups and diabetes tests. According to the American Diabetes Association, everyone ages 45 and older should undergo diabetes tests. However, testing is suggested at any age if you have one or more risk factors for diabetes, including a sedentary lifestyle, being overweight or obese, family history, and poor diet. The diabetes test is often a simple blood test. For normal results, repeat screening is advised every three years. If diagnosed early, Type 2 diabetes is manageable. A wide range of medications are available to reduce blood sugar levels. Whatever your diabetes reasons, these medicines are equally effective in reducing blood sugar levels. Diabetes medicines such as Glycomet 250, Invokana 100 mg, Trajenta 5mg, Metformin, Bigomet 500 mg, Glimepiride, Oxramet XR10/1000 mg, pioglitazone, Glipizide, and many more are available at affordable rates online. A healthy diet, lifestyle changes, and regular exercise can go a long way in managing the health problem.
Conclusion
Early diagnosis and treatment are important for improving overall quality of life and reducing your risk of developing severe complications. Primary diabetes prevention is feasible, and lifestyle modifications are effective for populations of varied ethnicities.