Whenever the body is up against any noxious stimuli, its in-built defense mechanism tries to counter the noxious stimuli to protect us from its ill effects. Noxious stimuli such as pathogens or toxins may damage cells resulting in inflammation.When cells get damaged, the immune response generates inflammation.The primary goal of such an inflammatory response is to remove the cause of cell injury or to remove the necrotic cell and tissue. Inflammation helps in initiating tissue repair.
Not only external stimuli like bacteria, virus, etc., stimulate inflammatory responses, but in certain diseases too, the immune system of the body triggers an inflammatory response. In such a condition when the body is under attack from within and not some external agent, the body’s own protective immune system starts to damage its tissue and this condition is known as autoimmunity. Rheumatoid arthritis is one such a disease in which the body’s own protective immune system starts to damage its tissue.
Also read: Arthritis – Don’t Make Joint Pain An Old Age Companion
How inflammation occurs?
When any foreign substance affects the body, chemicals from the body’s white blood cells are discharged into the blood or affected tissues to protect the body. The released chemicals increase the blood flow to the area of infection or injury, producing redness and warmth. These chemicals may cause fluid to leak into the tissues, which results in swelling. This protective process stimulates nerves causing pain.
Inflammation may be acute or chronic:
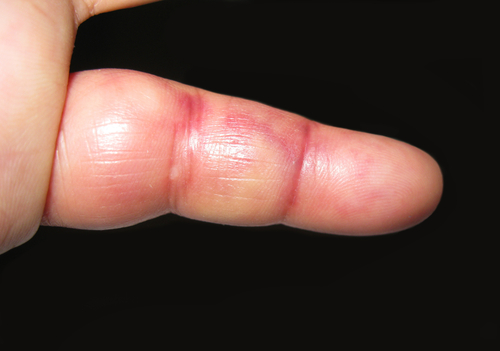
Acute inflammation: It is a rapid response to an injury or surgery usually in very little time .Redness, heat, pain, swelling, and loss of function are the five main indicators of acute inflammation that appears rapidly.
Chronic inflammation: Any condition that causes acute inflammation if not resolved, may persist for a long time. Chronic inflammation may be the result of several diseases like cancer, heart disease, diabetes, depression, allergies, chronic kidney disease, osteoporosis, and cognitive decline.
Risk Factors for Chronic Inflammation:
• Age
• Obesity
• Diet
• Low level of sex hormone
• Smoking
• Sleep disorder
Treatment of chronic inflammation:
Few available drugs to treat chronic inflammation are as below:
• Pentoxifylline
• Metformin
• Aspirin
• Low-Dose Statin Drugs
What are the treatments available?
The components of inflammation such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 can cause damage to healthy tissue. A balanced diet probably reduces these components of inflammation. Some tips for treating chronic inflammation through a proper and healthy diet are given below:
• Fat, mainly abdominal fat produces inflammatory cytokines and could very well be a reason of systemic inflammation. So it is very necessary that the total intake of energy should be proportional to total consumption to avoid any storage of abdominal fat.
• Various nutrients like Sesame Lignans, beta-carotene, genistein, Fish Oil and tea are the most effective anti-inflammatory nutrients.
• Multiple cytokines and pro-inflammatory molecules can be lowered by expending energy through exercise.
• Some studies reveal that the daily intake of fibrous food is helpful in the reduction of inflammation.
• Micronutrients like Magnesium, Vitamin D & E, Zinc and Selenium have nflammatory mediators properties.
• Bromelain is rich in plant enzymes and assists the body as a catalyst for repairing of cells.These enzymes can break down the byproducts of inflammation when they are taken on an empty stomach thus clearing the way for cellular repair.
• Take a diet low in Omega 6-rich foods like baked goods, meat, dairy, flour products, and grains when looking to relieve inflammation.
• Turmeric (curcumin) and garlic are anti- inflammatory spices that can ease signs of inflammation.
• Take nuts and fruits inbetween meals.Sunflower seeds, walnuts, almonds and hazelnuts are all good choices. Fruits like apples, pineapple, blueberries,cherries, raspberries, and strawberries can help in relieving pain and other signs of inflammation.
• Fish like salmon, cod, halibut, snapper, tuna and bass that are high in omega-3 fatty acid reduce inflammation.
• Avoid grain fed and organic meat, take sufficient protein from grain free food.
Other options include physical therapy like, cold therapy, heat therapy, electrical stimulation, acupuncture and massage to treat pain and inflammation.
• Heat therapy increases the blood flow and brings flexibility in connective tissue.It decreases pain, muscle spasms, joint stiffness. Heat therapy may be a very good option for people who are suffering from inflammation due to arthritis.
• Cold therapy is useful to reduce acute inflammation. The limited exposure of cold reduces the temperature of an inflamed area.
• The condition of peripheral nerve injury or spinal cord disorder muscles leads to lack of proper nerve input resulting in stiffness and contraction. An electrical stimulus placed on the skin provides a form of a stimulus that causes the contraction in the muscle and reduces the spasm.
• Massage has the vital role in the treatment of chronic inflammation. Massaging with various herbal oils like Peppermint Rosemary, Sandalwood, Frankincense, Yarrow oil reduces inflammation and pain.
Also read:How to Improve The Immune System With Best Foods!
Final words:
Though inflammation is not a disease, it affects normal physiological functions in your daily life. Besides medicine, the cure of inflammation depends on what you eat. An effort to manage your diet and exercise regularly can deliver you from inflammatory pain.