As people age the possibility of their becoming prone to various health conditions increase. Gout is one such physical problem. Reports have suggested that between 1- 2% of the Western population may get affected by gout at some point in their life.
What is Gout?
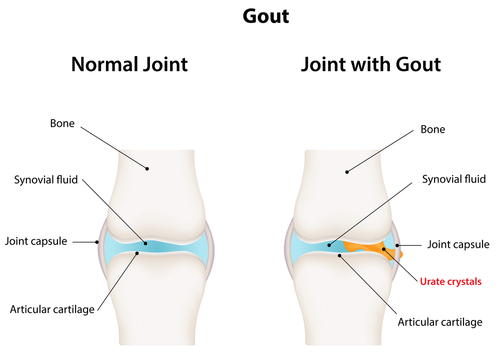
Gout is a complex form of arthritis, which is often characterized by sudden and severe attacks of pain, redness and tenderness in joints. The joints here mean the joint at the base of the big toe. Basically, gout can affect anyone, though research has shown that men are more prone to gout than women. But, reports have claimed that women become susceptible to gout after menopause.
Gout causes an acute attack that can wake you up in the middle of the night. You wake up with the sensation that your toe is on fire. This condition generally happens when there is a buildup of uric acid crystals in joints that causes sudden attacks of pain, swelling, and redness. When you are in the grip of this sensation even the weight of the light quilt on your joint may seem intolerable.
Also read: Arthritis – Don’t Make Joint Pain An Old Age Companion
Causes of gout:
Production of excess uric crystal levels in the blood is the main cause of gout. This condition may occur due to a number of reasons, including diet, drinking alcohol (especially beer), seafood, or taking medicines like aspirin or some diuretics. There are other causes of gout including genetic predisposition or under excretion of urate – the salts of uric acid.
Under excretion, as the name suggests is a condition in which less uric acid is excreted from the body. This condition is due to lesser excretion of uric acid by the kidney, which is the primary cause of hyperuricemia in 90% cases. Overproduction of uric acid occurs in less than 10% people. Moreover, the risk depends on the degree of hyperuricemia. When the levels are between 415 and 530 μmol/l and 7 and 8.9 mg/dl, the risk is said to be 0.5% per year, while in people whose levels are greater than 535 μmol/l or 9 mg/dL, the risk is said to be 4.5% per year.
Complications of gout:
There are a number of serious complications associated with gout. These include:
- Recurrent gout- Various people with gout may never experience any signs and symptoms, but some may experience gout several times each year. This condition may be controlled with medication and other preventive measures.
- Advanced gout- If gout remains untreated, the uric acid crystals can build up in the joints and nearby tissues and forms hard lumpy deposits called tophi. These may develop in areas like fingers, feet, hands, or elbows. Tophi is not painful, but it leads to swelling and tenderness of the tophi-affected body parts during gout attacks.
- Kidney stones- High levels of uric acid in the urinary tract of people may cause kidney stones or even kidney failure.
Also read: Menorrhagia: Menstrual Disorder in women
Before recommending any treatment option, your physician will perform certain tests. These include:
- Joint fluid test- In this test a needle is used to draw fluid from the affected joint. The sample is then examined under the microscope for urate crystals.
- Blood test- This test is done for measuring uric acid levels in blood. Test results may reveal surprising truths as some people with high uric acid levels may have never experienced gout attacks, whereas some people experience signs and symptoms of gout without having unusual levels of uric acid in their blood.
Gout treatment and medications:
Gout treatment usually involves medication. The medication depends on the state of your current health and your own preferences. Medication for gout is used to treat acute attacks and to prevent future attacks and aslo reduce complications of gout like development of tophi from urate crystal deposits.
Some gout medication includes:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) – NSAIDs are fairly popular among patients with gout, as these help in controlling inflammation and pain. Medication including Ibuprofen and Naproxen are often prescribed by physicians to lower the risk of gout attacks. A powerful (prescription) drug for treating gout is Indomethacin, which is used to treat severe gout attacks. Some common side effects of NSAIDs include stomach pain, bleeding and ulcers.
- Colchicine- This medicine is a type of pain reliever that reduces gout pain soon after the symptoms appear. Basically, Colchicine is prescribed to those patients who can’t take NSAIDs. This medicine is prescribed by the doctors to prevent future attacks.
- Corticosteroids- Corticosteroid medication is for those patients who are unable to take either NSAIDs or Colchicine. Corticosteroid is very helpful in controlling gout inflammation and pain. Physicians may prescribe this medication in pill form or in the form of injections. Some of the side effects of corticosteroids include poor wound healing, thinning of bones, and decreased ability to fight against infections. To reduce the risk of side effects, your physician may prescribe medication that may control the symptoms and prescribe steroids for the shortest possible time.
Also read: Understand Inflammation and Remain Pain- Free
Medications to prevent the complications of gout:
Below are various medications that may be recommended by your physician to reduce the risk of gout-related complications. These are as follows:
- Drugs or medication that block or reduce the production of uric acid include Xanthine oxidase inhibitors such as Allopurinol and Febuxostat. These medicines work by limiting the amount of uric acid the body makes.
- Probenecid medication improves the kidneys’ ability to remove the uric acid from body. Side effects of taking this medicine include rash, stomach pain and kidney stones.
Remedies for gout:
Long association with an unhealthy diet is the main cause of gout, particularly over indulgence of seafood, meat, and alcohol. The gout diet given here can help you maintain healthy weight and avoid several chronic diseases:
- Limit meat, poultry and fish –These food items are high in purines, which occurs when your body produces uric acid. Avoiding high-purine foods like organ meats, fatty fish and seafood (tuna, shrimp, and scallops) and red meat including beef, pork and lamb help decrease the risk of gout.
- Eat healthy- Eating a healthy diet by cutting back on fat promotes good health. When people eat saturated fats, their body’s ability to excrete uric acid becomes low. To lower the risk of gout attacks, you need to choose plant-based protein diet including beans and legumes and low-fat dairy products.
- Drink Fluids – Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water keeps the body hydrated and also washes away other health related problems. Water helps in removing uric acid from body, which is possible if you drink 8 to 16 glasses a day. Additionally, it has also been researched that drinking four to six cups of coffee a day lowers the risk of gout in men.
- Cherries- Cherries are regarded as natural home remedy or natural treatment option for treating gout. Studies have revealed that eating cherries lower the levels of uric acid in the body. Apart from eating cherries, there are other dark-colored fruits that may help in treating gout attacks. These include blueberries, purple grapes, blackberries, and raspberries.
Also read: How to Improve The Immune System With Best Foods!