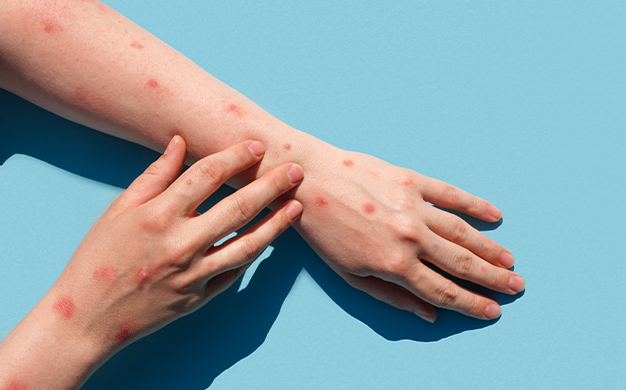
Monkeypox has been declared a health emergency in the world. It’s another pandemic terrorizing the people and administration. People suffering from monkeypox experience rash that may be located on or near the genitals (penis, testicles, labia and vagina) and could be on other areas like the hands, feet, chest, face, or mouth. The rashes may be painful or itchy and look like pimples or blisters. The rash goes through several stages, including scabs, before healing.
Symptoms of Monkeypox include:
- Chills
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Exhaustion
- Muscle aches and backache
- Headache
- Respiratory disorders
The symptoms differ from person to person, and there can be the appearance of some symptoms or all in the patient.
After COVID-19, monkeypox has created fear and paranoia in public, causing the development of monkeypox myths and misinformation. People have less information on the monkeypox virus facts because informatory releases and articles are not much available on the internet. This page will help you grab some important details on monkeypox myths and facts.
Monkeypox virus infection myths
- Myth – Scientists created monkeypox in a lab
Fact – Monkeypox is transmitted from animals to humans and is a zoonotic disease. There is no information regarding which animal acts as the reservoir for monkeypox or how it was transmitted to a human, and scientists in a lab did not create it. Monkeypox and smallpox belong to the same family of viruses and have historically been associated with travel to certain countries in central and western Africa, where it is considered endemic.
- Myth – Monkeypox is a new disease
Fact – The first human case of monkeypox was documented in the 1970s, and it was first discovered in 1958 in monkeys (hence the name).
- Myth – You can get monkeypox from a swimming pool
Fact – Monkeypox is a transmissible disease, but you cannot get it from a swimming pool. Monkeypox is transmitted through direct contact with infected animals or humans. And you can get infected with monkeypox by using the infected person’s things or contacting their body fluids.
- Myth – Monkeypox spreads through the air, and you can get infected with monkeypox from being in a crowd.
Fact – Monkeypox virus does not linger in the air for longer and is not transmissible through the air. So it’s highly unlikely to get an infection by walking through a crowded restaurant or store. But being in a tight space with the infected person and getting in contact with the infected person can get you the infection. Monkeypox can also spread through saliva and large respiratory droplets, requiring prolonged face-to-face contact such as talking to or kissing the infected person.
- Myth – Monkeypox is a fatal disease
Fact – Monkeypox is milder and is only rarely fatal. But the disease may cause severe symptoms, which can be painful, and unpleasant symptoms, so it is wise to avoid infection.
- Myth – Only gay, lesbian and bisexual people get infected with monkeypox
Fact – No disease affects people according to their sexual preferences. Anybody with low immunity can get infected with monkeypox. People from the heterosexual group can also get infected; they should avoid having sex with multiple partners. It is very important to get the information from a verified source.
- Myth – The monkeypox vaccine is new
Fact – No vaccine being used to prevent the spread of monkeypox is new. A vaccine developed in 2007 for smallpox is used as a preventive measure against monkeypox. Imvanex/imvamune, was approved three years ago-in 2019 as a vaccine against monkeypox and smallpox. So, there is no new vaccine for monkeypox.
- Myth – vaccine is available for everyone
Fact – It is not true as it is difficult to produce vaccines for a large crowd and every age group; hence the vaccine is available for a limited group of people with certain eligibility criteria. The eligibility can be checked through any verified government health site or with your physicians.
- Myth – Monkeypox is related to COVID-19
Fact – The only similarity between COVID-19 and monkeypox is that they both are viruses; other than this, they are different diseases. COVID-19 is part of the coronavirus family, whereas monkeypox is part of the Orthopoxvirus genus, a separate virus group.
- Myth- Monkeypox is a sexually transmitted disease.
Fact – Monkeypox can be easily spread through bodily fluids and easily transmitted through sexual activity. Misinformation is saying transmission is exclusively sexual.
- Myth – There is no need to isolate the infected person.
Fact – The disease spreads by coming in direct contact with an infected person, so it is very important to isolate the infected person. Monkeypox is heavier than COVID-19, so they cannot travel a long distance; hence it is important to get isolated, decreasing the risk of spreading infection.
Takeaway
As more cases emerge, a slew of monkeypox virus infection myths emerges. Knowing the right information about the disease is crucial so it can be easily prevented. Avoiding contact with the infected person is very important. Lead a healthy lifestyle and take the required prevention to reduce the risk of the Monkeypox epidemic.